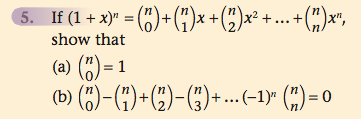SEARCH THIS BLOG :-)
Monday, 30 November 2015
Thursday, 26 November 2015
Tuesday, 24 November 2015
GROVE HSC 3U EX2.8 - REGARDING Q15
JUst regarding finding the second derivative of this (good luck to you!)
WOLFRAM ALPHA SAYS
AND THIS CAN NEVER BE ZERO, SO THERE ARE NO INFLEXIONS.
(yes x here should be h)
GROVE HSC 3U - EX2.8 - SIMILAR QUESTION
Question: Find any non horizontal inflexions.
(by finding second derivative)
[this is not Q15, but looks similar.
It's good practice for derivatives]
Monday, 23 November 2015
GROVE HSC 3U TEST YOURSELF 10 - Q13
Sunday, 22 November 2015
GROVE HSC 3U - TEST YOURSELF 10 - Q5
(a) Put $x=0$ on LHS and RHS!
(b) Put $x=-1$ on LHS and RHS!
Keep in mind $(-1)^2=1$, $(-1)^3=-1$, $(-1)^4=1$, ...
Saturday, 21 November 2015
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U TEST YOURSELF 8 - Q18
$y={1\over 3}x^{-1}$
$y'=-{1\over 3}x^{-2}$
$y'=-{1\over 3x^2}$
$y'=-{1\over 3\left({1\over 6}\right)^2}=-{36\over 3}=-12$
When $x=1/6$, $y=1/(3(1/6))=2$
$y-2=-12(x-1/6)$
$y-2=-12x+2$
$y'=-{1\over 3}x^{-2}$
$y'=-{1\over 3x^2}$
$y'=-{1\over 3\left({1\over 6}\right)^2}=-{36\over 3}=-12$
When $x=1/6$, $y=1/(3(1/6))=2$
$y-2=-12(x-1/6)$
$y-2=-12x+2$
$12x+y-4=0$
JH :-)
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U TEST YOURSELF 8 - Q20
$y'={vu'-uv' \over v^2}$
$y'={(2x+1)4-(4x-3)2 \over (2x+1)^2}$
Put $x=1$
$y'={(2(1)+1)4-(4(1)-3)2 \over (2(1)+1)^2}$
$y'=\displaystyle{10\over 9}$
When $x=1$, $y=(4-3)/(2+1)=1/3$.
$(1, 1/3)$.
$y-{1\over 3}={10\over 9}(x-1)$
$9y-3=10(x-1)$
$9y-3=10x-10$
$10x-9y-7=0$
When $y=0$,
$10x-7=0$
$x=\displaystyle {7\over 10}$
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U TEST YOURSELF 8 - Q15
Find $y'$ then sub $x=2$
Use product rule: If $y=u(x)\times v(x)$ where $u,v$ are functions of $x$, then
$$y'=uv'+u'v$$
Here $$u(x)=(3x-1)^3, v(x)=(2x-1)^2$$$y'=(3x-1)^3\times 2(2x-1)\times 2\\+3(3x-1)^2\times 3(2x-1)^2$
$y'=(3(2)-1)^3\times 2(2(2)-1)\times 2\\+3(3(2)-1)^2\times 3(2(2)-1)^2$
$y'=3525$
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U EX 8.9 - Q8
$y'=2(x+3)^2+2x\times 2(x+3)$
$y'=2(x^2+6x+9)+4x^2+12x$
$y'=2x^2+12x+18+4x^2+12x$
$y'=6x^2+24x+18$
$\therefore 6x^2+24x+18=14$$6x^2+24x+4=0$
$3x^2+12x+2=0$
$x=\displaystyle { -12\pm \sqrt{12^2-4(3)(2)} \over 6}$
$x=\displaystyle { -12\pm \sqrt{120} \over 6}$
$x=\displaystyle { -12\pm 2\sqrt{30} \over 6}$
$x=\displaystyle { -6\pm \sqrt{30} \over 3}$
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U TEST YOURSELF 8 - Q15
QUESTION:
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve $y=x^2+2x-5$ that is parallel to the line $y=4x-1$.
SOLUTION:
We need to find the $x$ value on the curve at which the tangent has gradient $m=4$
(since the line $y=4x-1$ has gradient $4$)
(since the line $y=4x-1$ has gradient $4$)
Find $y'$.
(since $y'$ is the gradient of the tangent at $x$)
(since $y'$ is the gradient of the tangent at $x$)
$y'=2x+2$
Solve $y'=4$.
$2x+2=4$
$2x=2$
$x=1$
When $x=1$, $y=(1)^2+2(1)-5=-2$
So the point is $(1,-2)$.
Tangent has equation $y-y_1=m(x-x_1)$
$$y--2=4(x-1)$$
$$y+2=4x-4$$
$$4x-y-6=0$$
GROVE PRELIM 2U/3U BOOK - TEST YOURSELF 8 - Q13
Regarding $\pi$ as a constant and differentiating with respect to $x$.
$${dS\over dr}=2\times 4\pi r^{2-1}$$
$${dS\over dr}=8\pi r^{1}$$
$${dS\over dr}=8\pi r$$
C'est fini.
JH
Firstly, the question should read, "find a quadratic equation...." as there are many....
(a)
$(x-4)(x- -7)=0$
$x^2-4x+7x-28=0$
$x^2+3x-28=0$
(b)
$(x-5-\sqrt{7})(x-5+\sqrt{7})=0$
$((x-5)-\sqrt{7})((x-5)+\sqrt{7})=0$
Thin difference of two squares.
$(x-5)^2-\sqrt{7}^2=0\\$
$(x-5)^2-7=0\\$
$x^2-10x+25 -7=0\\$
$x^2-10x+18=0$
$(x-5-\sqrt{7})(x-5+\sqrt{7})=0$
$((x-5)-\sqrt{7})((x-5)+\sqrt{7})=0$
Thin difference of two squares.
$(x-5)^2-\sqrt{7}^2=0\\$
$(x-5)^2-7=0\\$
$x^2-10x+25 -7=0\\$
$x^2-10x+18=0$
GROVE HSC 3U - TEST YOURSELF 9 (APPROX OF ROOTS) - Q6
It's up to you to find to values of $x$ such that the function value changes sign.
It will be easy trial and error. (unlikely in an actual test)
Let's randomly (with a bit of intuition) try $x=0$ and $x=2$!
$f(x)=x^3+3x-7$
$f(0)=-7<0$
$f(2)=2^3+3(2)-7=8+6-7=7>0$
Since $f(0)<0$ and $f(2)>0$, then there is at least one root between $x=0$ and $x=2$.
Now proceed to half the interval 3 times.....
GROVE PRELIM 2U TEST YOURSELF 9 / GROVE PRELIM 3U TEST YOURSELF 10 - Q13
Multiply both sides by $x$.
$\displaystyle 2x=5+{3\over x}$
$\displaystyle 2x\times x=5\times x+{3\over x}\times x$
$$2x^2=5x+3$$
$$2x^2-5x-3=0$$
$$2x^2-6x+1x-3=0$$
$$2x(x-3) + 1(x-3)=0$$
$$(2x+1)(x-3)=0$$
$$\therefore x=-0.5, 3$$
JH2015 :-)
Grove HSC 2u Chapter 2 Test Yourself 2 Q15
Labels:
2u,
BOSTES,
Chapter 2,
Grove,
HSC,
maxima minima problem,
Q15,
Test Yourself 2
Friday, 20 November 2015
GROVE HSC 3U (APPROX OF ROOTS) EX 9.1 - Q10 -
Monday, 16 November 2015
GROVE HSC CHALLENGE EX2 - Q2 - Curve sketching, stat points, inflexions
Sunday, 15 November 2015
Saturday, 14 November 2015
Quadratic Identity question
QUESTION:
Write $3x^2+7$ in the form $a(x-2)^2+b(x+3)+c$.
ANSWER:
$3x^2+7=a(x-2)^2+b(x+3)+c$ holds for all $x$.
Best way is to just expand the RHS and then equate coefficients of the powers of $x$ on LHS and RHS.
$3x^2+7=a(x^2-4x+4)+b(x+3)+c$
$3x^2+7=a x^2-4ax+4a+bx+3b+c$
$3x^2+7=a x^2+(b-4a)x+(4a+3b+c)$
Write $3x^2+7$ in the form $a(x-2)^2+b(x+3)+c$.
ANSWER:
$3x^2+7=a(x-2)^2+b(x+3)+c$ holds for all $x$.
Best way is to just expand the RHS and then equate coefficients of the powers of $x$ on LHS and RHS.
$3x^2+7=a(x^2-4x+4)+b(x+3)+c$
$3x^2+7=a x^2-4ax+4a+bx+3b+c$
$3x^2+7=a x^2+(b-4a)x+(4a+3b+c)$
Therefore
- $a=3$ (comparing coefficient of $x^2$ on LHS and RHS)
- $b-4a=0$ since coefft of $x$ on LHS is 0. (there is no $x$ term)
- $4a+3b+c=7$ (Constant terms on LHS and RHS)
So, $b-4(3)=0$.
$b=12$.
Finally, $4(3)+3(12)+c=7$.
So, $c=7-12-36=-41$.
Final answer: $a=3, b=12, c=-41$.
Friday, 13 November 2015
Grove HSC 3U EX 10.4 - Q3, 9, 11c, 15, 16, 18a, 20ac, 21abe -: Binomial Theorem
QUESTIONS: Q3, 9, 11c, 15, 16, 18a, 20ac, 21abe,
Q3 =====================
 | ||
| Fanks Tatiana :-) Q9 =====================
|
Q15 =====================
Q16 =====================
Q18a =====================
 |
Thanks Juliette :-) |

Q20c =====================
This is a second version of this solution.
 |
| Thanks Tat & Ellie
Q20c - version 2-=====================
Q21a=====================
Q21b =====================
Q21e =====================
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)